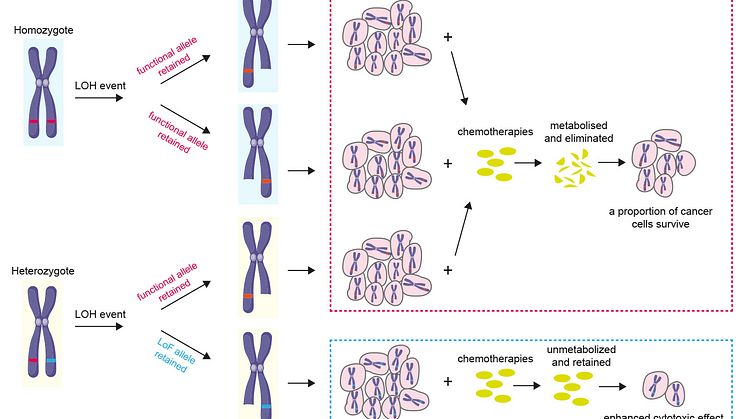
Breast cancer risk varies between different hormonal contraceptives
Some common hormonal contraceptives are linked to a slightly higher risk of breast cancer than others. This is shown by a new Swedish study from Uppsala University, in which researchers followed more than two million women and teenage girls in Sweden to identify how different hormonal contraceptives affect the risk of breast cancer.