New antibody could be promising cancer treatment
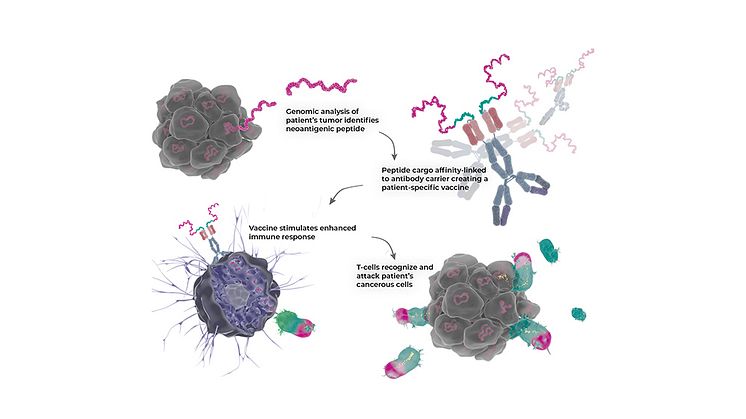
Researchers at Uppsala University and KTH Royal Institute of Technology have developed a new form of precision medicine, an antibody, with the potential to treat several types of cancer. Researchers have managed to combine three different functions in the antibody, which together strongly amplify the effect of T cells on the cancer tumour. The study has been published in Nature Communications.