Press release -
Researchers discover ‘epic’ new Burgess Shale site in Canada’s Kootenay National Park
Yoho National Park’s 505-million-year-old Burgess Shale – home to some of the planet’s earliest animals is one of the world’s most important fossil sites. Now, more than a century after its discovery a new Burgess Shale fossil bed, Marble Canyon, has been located 42 kilometres away in Kootenay National Park.
A paper published today in the prestigious scientific journal Nature Communications describes Kootenay National Park’s new ‘Marble Canyon’ fossil beds for the first time. The authors suggest that the area and its extraordinary fossils will greatly further our understanding of the sudden explosion of animal life during the Cambrian Period.
The find was made in the summer of 2012 by a team from the Royal Ontario Museum (ROM, Jean-Bernard Caron), Pomona College (Robert Gaines), the University of Toronto (Jean-Bernard Caron, Cédric Aria), the University of Saskatchewan (Gabriela Mángano) and Uppsala University (Michael Streng).
“This new discovery is an epic sequel to a research story that began at the turn of the previous century. There is no doubt in my mind that this new material will significantly increase our understanding of early animal evolution,” said Dr. Jean-Bernard Caron, Curator of Invertebrate Paleontology at the ROM, Associate Professor at the University of Toronto and the study’s lead author. “The rate at which we are finding animals – many of which are new – is astonishing, and there is a high possibility that we’ll eventually find more species here than at the original Yoho National Park site, and potentially more than from anywhere else in the world.”
In a short 15-day field season, the researchers collected thousands of specimens representing more than 50 species, several of which were new to science. Incredibly, many of the species previously known from Yoho are better preserved in Kootenay, retaining very fine, never-before-seen anatomical details that are important for understanding the shape of the animal ‘family tree.’
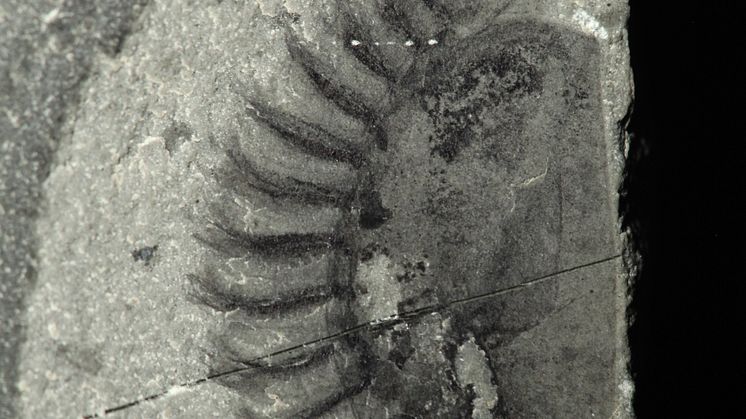
The new site parallels Yoho in its spectacular richness of arthropods, a group that today represents more than 80% of all living animals, including insects, spiders and lobsters.
Another curious similarity between Marble Canyon and the original discovery is that both sites would still be buried today if not for the dedicated exploratory work of scientists.
In 1909, world-renowned paleontologist Charles Walcott spent a summer exploring Yoho National Park’s mountainous topography in search of hidden treasures, only to stumble upon what he would later name the Burgess Shale on the final day of his field season on August 29. Similarly, in 2012, a ROM field expedition led by Caron spent part of their summer in search of the next big paleontological discovery.
“We were already aware of the presence of some Burgess Shale fossils in Kootenay National Park,” said Dr. Robert Gaines, a geologist from Pomona College, who along with Caron and colleagues had spent August 2008 at a much smaller fossil deposit in the park located near Stanley Glacier. “We had a hunch that if we followed the formation along the mountain topography into new areas with the right rock types, maybe, just maybe, we would get lucky – though we never in our wildest dreams thought we’d track down a motherload like this.”
"The new site is clearly a finding of a lifetime. The intriguing part about the discovery is that it parallels in many ways the anecdotes surrounding the original discovery of the Burgess Shale by Charles D. Walcott in 1909. Although no stumbling horse is part of our story, it was one of these amazing and fortunate last minute discoveries. The terrain was rough, the rock exposure poor, and the rocks we had seen all day weren’t promising at all" says Michael Streng, researcher at Department of Earth Sciences, Uppsala University
"It was when we discussed if we should go back to camp never to return to this part of the mountains again, that Bob Gaines discovered arthropod remains on a piece of rock lying on the ground. Immediate excitement was in the air. When a hit with the hammer on another piece of rock exposed an arthropod with previously unseen details, we knew we were really on to something. The hunt was on!"
The new fossil site is protected by Parks Canada, with the exact location remaining confidential to protect its integrity. Future visitor opportunities have not been ruled out.
To learn more about the Burgess Shale visit this award-winning website: www.burgess-shale.rom.on.ca
Contacts
Dr. Jean-Bernard Caron (bilingual)
Curator of Invertebrate Palaeontology, Royal Ontario Museum
And
Associate Professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary
Biology and the Department of Earth Sciences, University of Toronto
416 586 5593; jcaron@rom.on.ca
Dr. Robert Gaines
Associate Professor of Geology, Pomona College
Office: 909 621 8674, Cell: 909 451 3073; robert.gaines@pomona.edu
Dr. Michael Streng
Department of Earth Sciences, Uppsala University
+46 70-9622588 or +46 18-4712579; michael.streng@geo.uu.se
David McKay
Communications Coordinator
Royal Ontario Museum
416 586 5559; davidm@rom.on.ca
Jennifer Thoma
Media Relations Specialist
University of Saskatchewan
306-966-1851; jennifer.thoma@usask.ca
Omar McDadi
Public Relations and Communications Officer
Parks Canada, Yoho and Kootenay national parks
403 760 1090; omar.mcdadi@pc.gc.ca
Burgess Shale facts:
• This new finding is the latest in a recent string of Burgess Shale discoveries, including confirmation that Pikaia, found only in Yoho National Park, is the most primitive known vertebrate and therefore the ancestor of all descendant vertebrates, including humans.
• In over 100 years of research, approximately 200 animal species have been identified at the original Burgess Shale discovery in Yoho National Park in over 600 field days. In just 15 days of field collecting, 50 animal species have already been unearthed at the new Kootenay National Park site.
• Some species found at the new Kootenay site are also found in China’s famous Chengjiang fossil beds, which are 10 million years older. This contributes to the pool of evidence suggesting that the local and worldwide distribution of Cambrian animals, as well as their longevity, might have been underestimated.
• The original Burgess Shale site in Yoho National Park was recognized in 1980 as one of Canada’s first UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Now protected under the larger Rocky Mountain Parks UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Burgess Shale attracts thousands of visitors to Yoho National Park each year for guided hikes to the restricted fossil beds from July to September. Both Parks Canada and the Burgess Shale Geoscience Foundation lead hikes to the fossils.
• All the Burgess Shale fossil specimens in the Marble Canyon area of were collected under a Parks Canada Research and Collection permit and are held in trust for Parks Canada at the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto.
Topics
Uppsala University -- quality, knowledge, and creativity since 1477
World-class research and outstanding education of global benefit to society, business, and culture.
Uppsala University is one of northern Europe's highest ranked academic institutions. www.uu.se