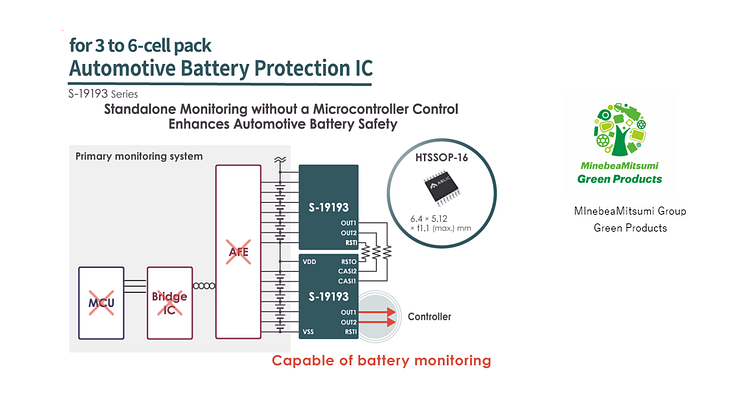
News -
<Topics> Functional Safety Challenges in Autonomous Vehicles
As autonomous driving systems advance, ensuring functional safety becomes increasingly critical. ABLIC, a manufacturer of analog semiconductors with over 20 years of experience in automotive electronics, offers insights into this complex issue from a component-level perspective.
Pursuing Zero Accidents in Autonomous Driving
Autonomous driving systems aim to reduce accidents caused by human error. However, as operational conditions expand and vehicles assume more driving responsibilities, creating entirely error-free and malfunction-proof systems becomes increasingly challenging.
Critical Systems and Potential Failures
Electric Power Steering (EPS)
In the case of EPS failure during autonomous operation, there is a risk of loss of vehicle control and an increased likelihood of lane departure. To mitigate this, the system switches to a subsystem that provides minimal steering assistance before transitioning to manual operation. However, even after control is transferred to the driver, the loss of power assistance significantly impairs operability, making it crucial to have robust fail-safe mechanisms in place.
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Through our work on power management ICs we have found that a failure in the drive train's BMS can necessitate an emergency stop, potentially causing high-speed collisions, especially with following vehicles.
These examples illustrate how component-level failures can lead to severe safety hazards, emphasizing the need for robust functional safety measures.
A Multi-Tiered Approach to Functional Safety
A multi-tiered approach is essential to address the challenges of functional safety in autonomous vehicles. This strategy emphasizes the importance of systems transitioning to a safe state when encountering unexpected situations. For example, EPS should switch to a subsystem, providing minimal steering assistance through a safety mechanism before transitioning to manual operation. Similarly, BMS should have a backup power supply to maintain critical functionalities. This layered approach provides redundancy, ensuring that multiple safety mechanisms are in place to prevent or mitigate potential accidents.
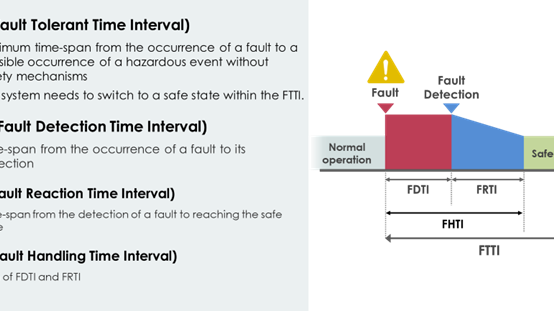
Transitioning to a safe state is a crucial process and involves three key steps: detection, notification, and handling. The time to complete these steps is critical and is regulated by the Fault Tolerant Time Interval (FTTI) as specified in ISO 26262.
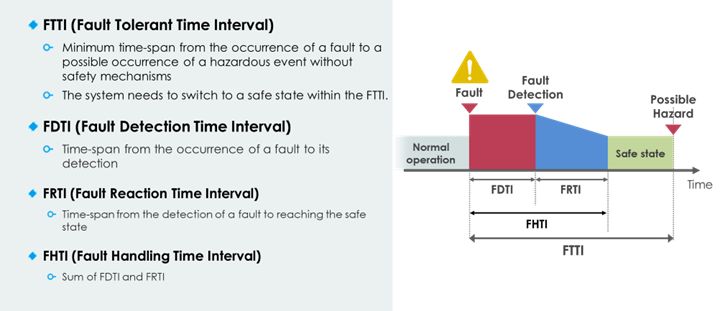
Detection involves identifying anomalies within the system. Notification is the process of communicating the detected anomaly to the relevant parts of the system responsible for managing faults. Handling is the final step where the system takes action to mitigate the detected issue. This could involve activating backup systems, adjusting operational parameters, or initiating a safe shutdown procedure.
Optimizing detection and notification can significantly enhance overall system safety. By optimizing these steps, particularly detection and notification, autonomous vehicle systems can have more time for appropriate fault handling. This additional time could allow for the implementation of more sophisticated safety mechanisms or enable new handling methods to enhance overall vehicle safety.
ABLIC: Advancing Safety Solutions for Autonomous Vehicles
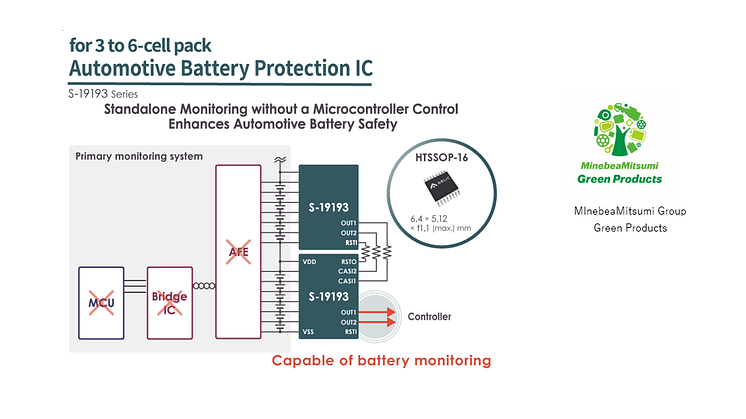
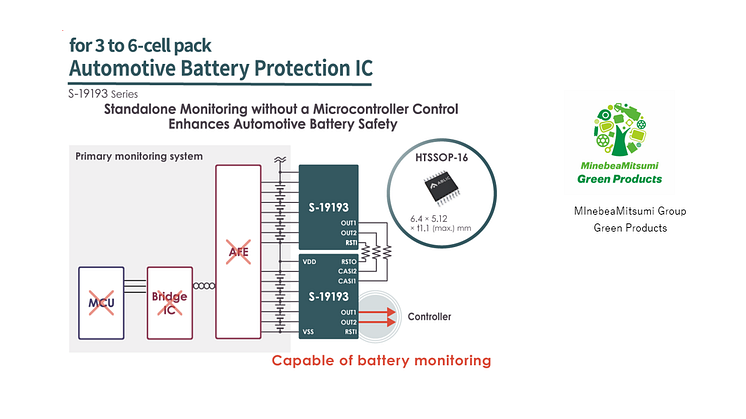
ABLIC, a specialized analog semiconductor manufacturer, has developed voltage monitoring ICs that detect and notify anomalies significantly faster than conventional products. These ICs can operate up to 20 times faster, directly contributing to meeting FTTI requirements in vehicles. This improvement allows for more time in fault handling, enabling complex safety mechanisms and new handling methods. The company's commitment to development process of functional safety is demonstrated by its ISO 26262 certification from SGS-TÜV Saar GmbH. To support automotive engineers who implement these safety measures, ABLIC provides technical support through its Frankfurt office.
As the automotive industry progresses towards higher levels of autonomous driving, the demand for specialized components that meet stringent safety requirements continues to grow. ABLIC's focus on high-speed, reliable voltage monitoring and analog semiconductor technology makes it a valuable contributor to the ongoing efforts to enhance the safety and reliability of autonomous driving systems.
Functional Safety Compliance
https://www.ablic.com/en/semicon/products/automotive/asil/fusa-compliance/?rf=ew2410